Data binding serves as a link between the template (representing the view) and the component (which contains the application's logic and data).

In Angular data binding, various types are used to define the direction of data flow between the component and the template (view).

Type of Data Binding
- One-way Data Binding
- Two-way Data Binding
One-way Data Binding
Interpolation

Interpolation is a simple and straightforward method for embedding dynamic values into HTML templates. It allows you to show component properties in the view.
Example
//app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule],
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrl: './app.component.css'
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'TodoList';
}
<!-- app.component.html -->
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
Property Binding

Property binding allows you to bind a property of a DOM element to a component property. This way, changes in the component automatically reflect in the view.
Example
//app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule],
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrl: './app.component.css'
})
export class AppComponent {
isDisabled= true;
}
<!-- app.component.html -->
<button [disabled]="isDisabled">Click me</button>
Event Binding
Event binding enables you to respond to user interactions or other events by connecting a component method with a specific event in an HTML template. This two-way link allows for dynamic and interactive user experiences by triggering component functions in response to user actions like clicks, hovers, touches, and other events.

Example
//app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, RouterOutlet],
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrl: './app.component.css'
})
export class AppComponent {
onClick() {
console.log(Hi Welcome!');
}
}
<!-- app.component.html -->
<button (click)="onClick()"> Click me 😊</button>
Two-way Data Binding
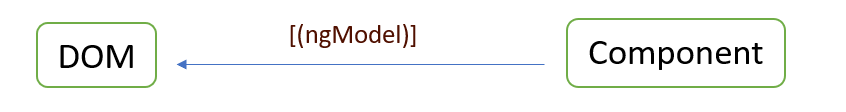
Two-way binding combines property and event binding to provide a bidirectional link between a component property and a template input element. This synchronization allows for automated updates in both directions, guaranteeing that changes to the component's properties are reflected in the template and vice versa, eliminating the need for explicit event handling or manual updates. To utilize [(ngModel)], you must import the FormsModule into your module, as it contains the directives required for two-way binding.
Example
//app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule,FormsModule],
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrl: './app.component.css'
})
export class AppComponent {
text: string = '';
}
<1 -- app.component.html -->
<input [(ngModel)]="text" placeholder="Please enter text here">
<p>the text which you have type: {{ text }}</p>
Data binding is essential for connecting the application's logic with the user interface, offering one-way bindings for efficient data transfer and two-way bindings, exemplified by [(ngModel)], for seamless bidirectional synchronization, streamlining the development of dynamic and interactive web applications.